Table of contents [hide]
MECHANISM
- Fold
- Compression
- Stretch.
CLASSIFY
Two large groups are high cervical spine injuries (C1, C2) and low cervical spine injuries (C3 → C7).
+ Type I: subsidence fracture
+ Type II: broken in many pieces
+ Type III: broken
- Treatment:
+ Type I - II: stable: neck brace - headband (3 months)
+ Type III: unstable: 3 months headband or occipital-neck welding surgery
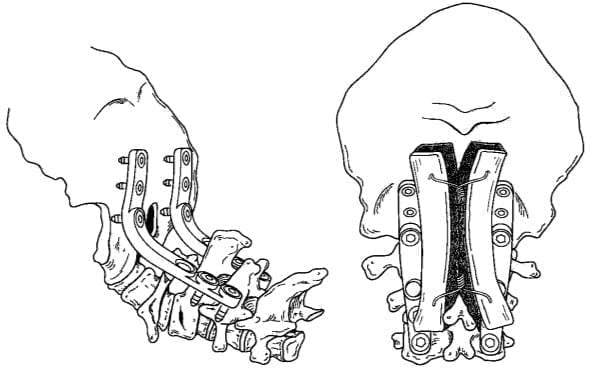
Figure 11.1. Neck occipital welding surgery
High cervical spine injury
Include fracture and skull dislocation (C0) with C1 and C1 with C2. These injuries include: skull fracture (C0), dislocation C0C1, dislocation or subluxation of C1C2, fracture C1, fracture of the cranium, fracture of arcuate C2.
C0 clubhead fracture: Classify
C1 . fracture
- Classify:
- + Broken posterior bow
- + Fracture 4 pieces (Jefferson)
- + Broken anterior bow
- + Fracture of transverse trowel
- + Fracture of the lateral block
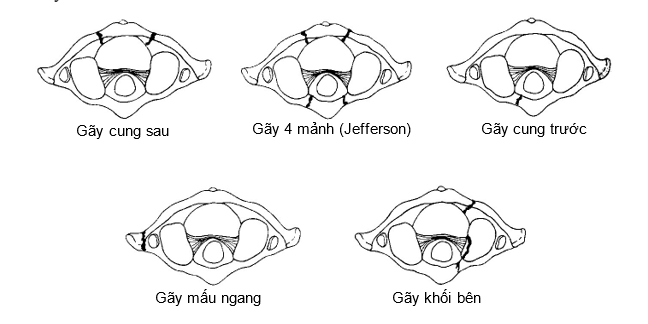
Figure 11.2. Classification of C1 . fractures
- Treatment:
- + From 2 to 7 mm: 3 months head circumference
- + Over 7mm:
- Conservation: pull the neck for 4-6 weeks, the shirt around the head for 2 months
- Surgery: rarely done, neck pulling + welding C1 – C2 (or C0 – C1)
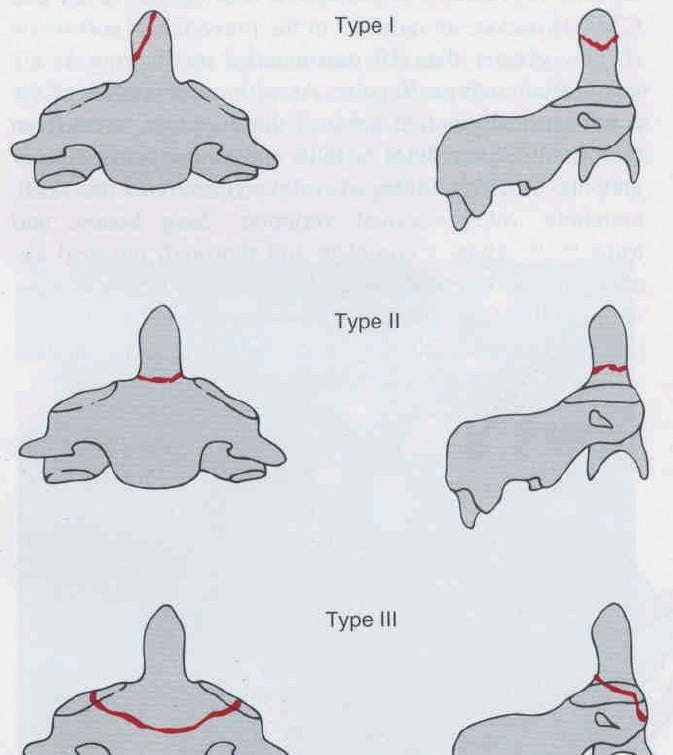
Figure 11.3. Classification of fractures according to Anderson and Alonzo
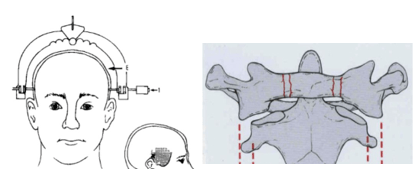
Figure 11.4. Horizontal displacement C1 – C2: X + Y
Broken tooth root
- Anderson and Alonzo classification
- + Type I: fracture of the crown of the tooth
- + Type II: broken tooth root
- + Type III: broken body C2.
- Treatment
- + Type I: 3 months neck brace
- + Type II: surgery + C2 screw removal (Figure 11.6A)
- Tie the steel thread and weld the C1 – C2 bones at the back (Figure 11.6B)
- + Type III: 3 weeks of neck pulling, a stiff neck brace or a full headband for 3 months
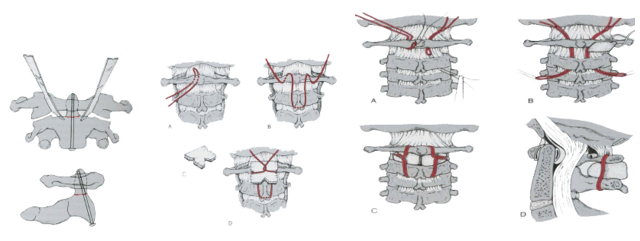
Figure 11.6. Catch the C2 (A) tooth screw, tie the steel thread and weld the C1 - C2 bone at the back (B)
Hangman's fracture C2
- – Classification (Figure 11.7)
- + Type I: fracture without displacement < 3 mm
- + Type II: fracture – displacement > 3 mm
- + Type III: fracture - dislocation C2 - C3.
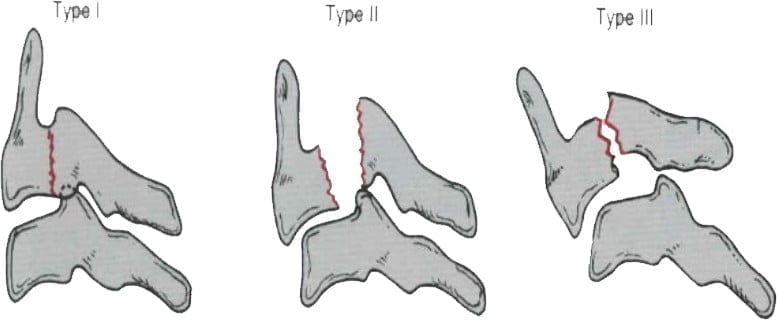
Figure 11.7. Classification of C2 . arch fracture
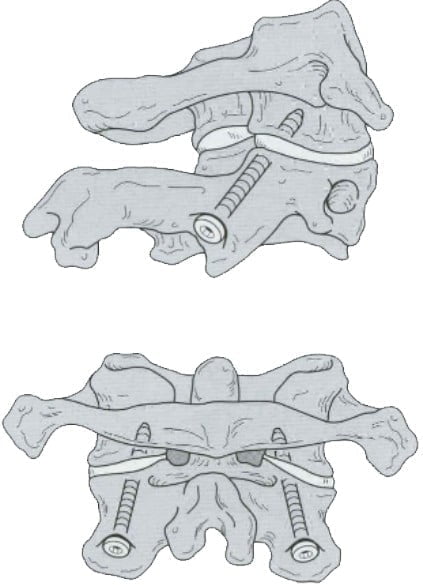
Figure 11.8. C2 . arthroplasty
- Treatment
- + Type I: neck brace - headband for 3 months
- + Type II - type III: conservation: pull - neck brace, headband
- Surgery: piercing the C2 trochanteric block (Figure 11.8)
Low cervical spine injury
- Classify:
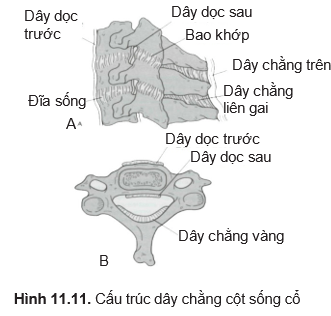
- + Damage to the posterior column
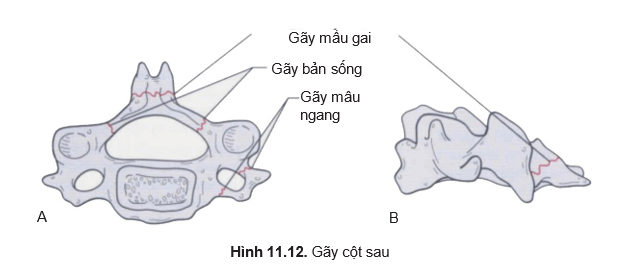
- Fracture: spine, vertebral column, transverse node (Figure 11.12)
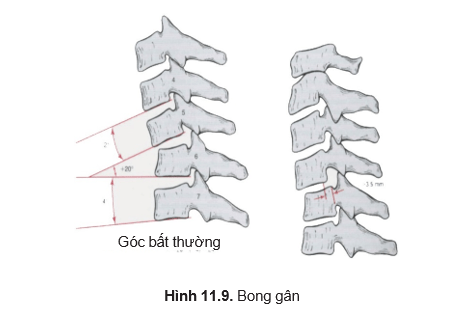
- Injury to ligaments: (Figure 11.9)
- Sprains light
- Severe sprain
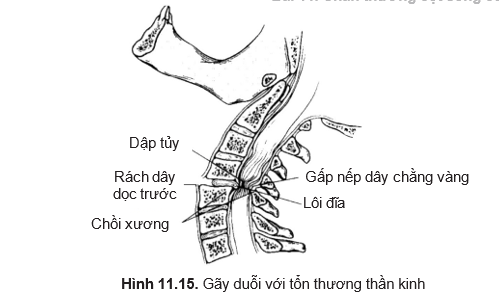
- Extensor fracture with nerve damage (Figure 11.15)
- + Injury to the joints
- Broken 1 joint or 1 arch
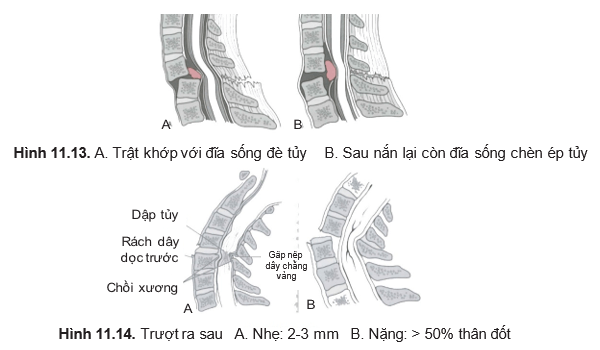
- Dislocation of 1 joint (Figure 11.13)
- Dislocated 2 joints
- + Anterior column damage
- Subsidence fracture
- Compression fracture with posterior ligamentous injury
- Disc-ligament injury
- Supine tear tear (fracture of vertebral body)
- Posterior sliding injury (Figure 11.14)
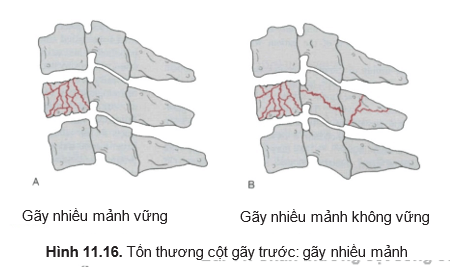
- Stable multi-fragmentation fracture (Figure 11.6A)
- Unstable multi-fragmentation fracture (Figure 11.6B)
- Broken tear drops.
- + Damage to the posterior column
- Treatment:
- + Goals:
- Extra injury protection: first aid correct
- Fix and fix
- Release pressure when there is pressure and keep it for a long time.
- + Principle:
- Recovery
- Assessment and classification of injuries
- Strong assessment – unsustainable
- Pinch early if possible
- Injury treatment
- Conserve
- Surgery: decompression – bone grafting – fixation.
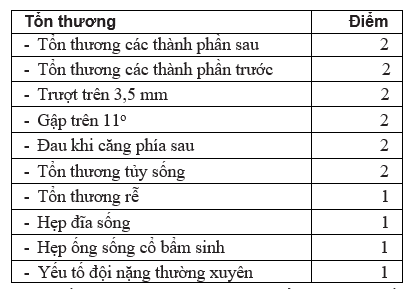
- + Specific treatment: assess instability when greater than 5 points.
- + Goals:
WHITE AND PANZABI STANDARDS
See also the White-Panjabi standard: White-Panjabi classification – WebNeurosurg
Treatment of stable fractures C3 – C7: stiff neck brace for 6-8 weeks (Figure 11.7)
X-ray after wearing the brace and every 2 weeks until heal bones (6 - 8 weeks)
Common types of stable fractures:
- Unsustainable standards White and Panzabi below 5 points
- Subsidence fracture
- Fracture at the front longitudinal wire attachment
- Broken tear stretch
- Mild sprain
- Isolated damage to the following components
Treatment of unstable fractures:
- Unstable, not oppressive:
- + Back bone welding + posterior bone fusion device (Figure 11.18)
- + Or intervertebral bone graft + anterior screw splint (Figure 11.19)
- Unstable with spinal cord compression:
- + Decompression + Intervertebral bone graft + anterior screw splint (Figure 11.20)
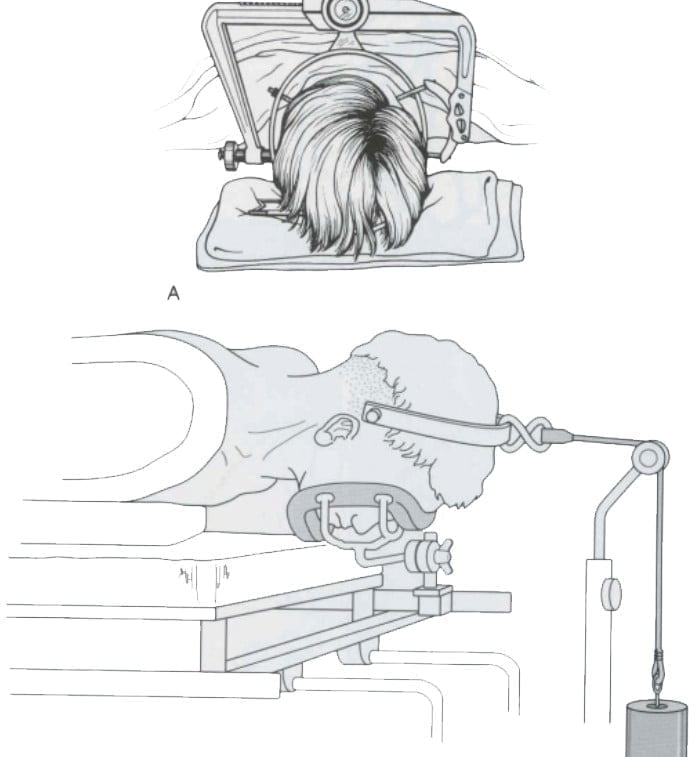
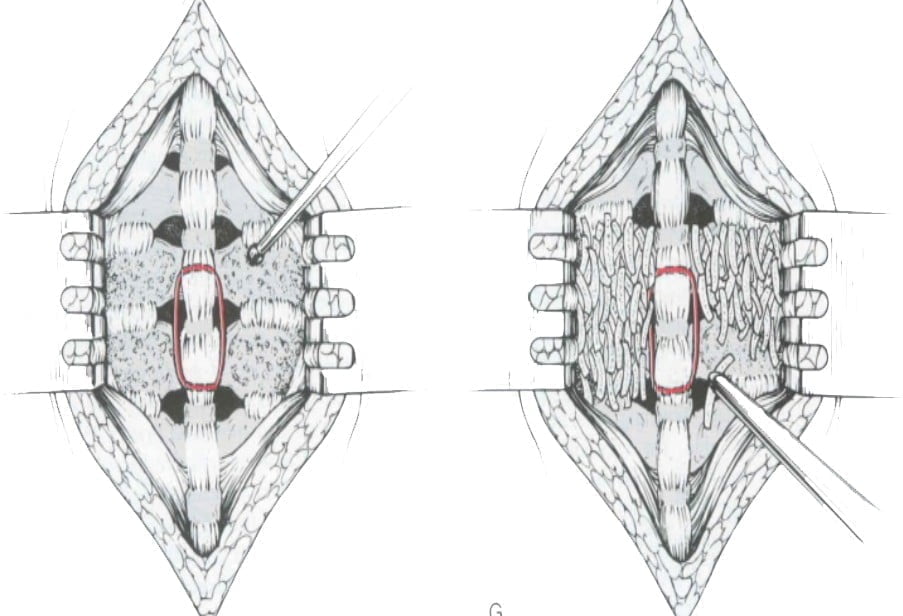
Figure 11.17. Rigid neck brace Figure 11.18. Rear steel thread presser and back welding
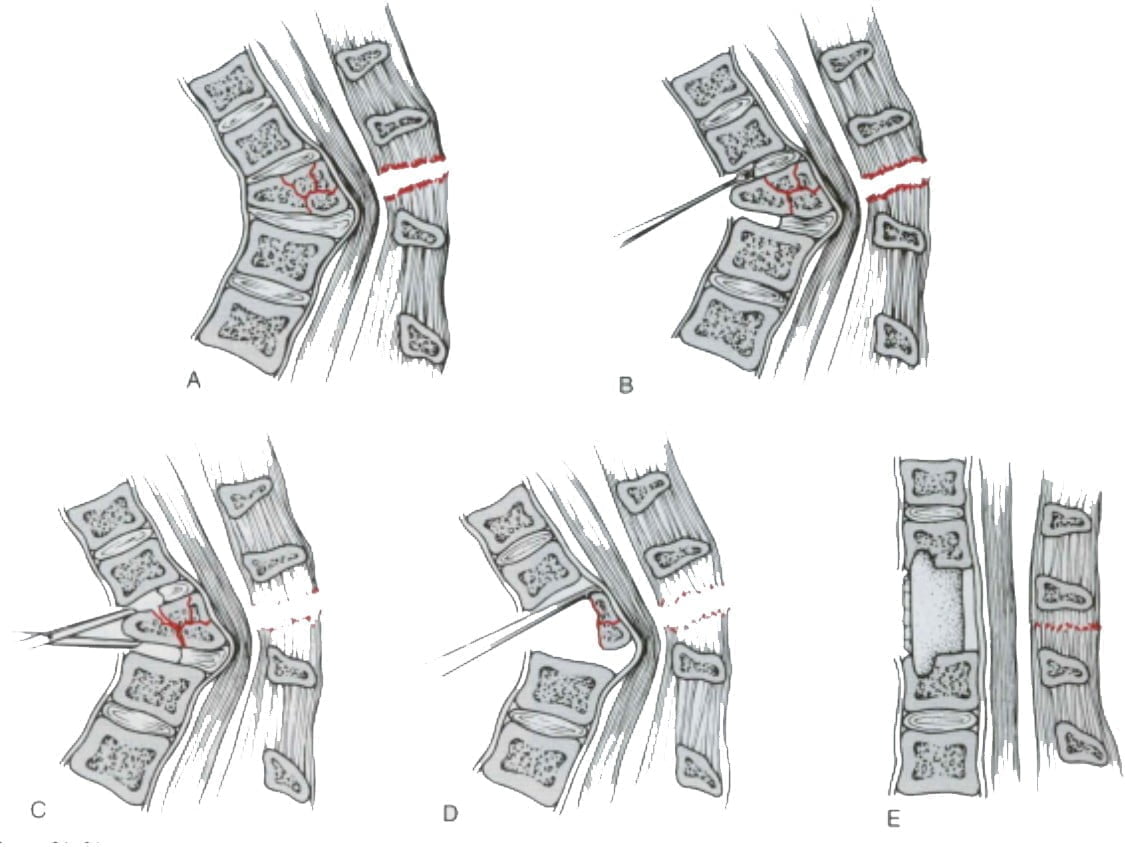
Figure 11.19. Decompression – anterior bone grafting
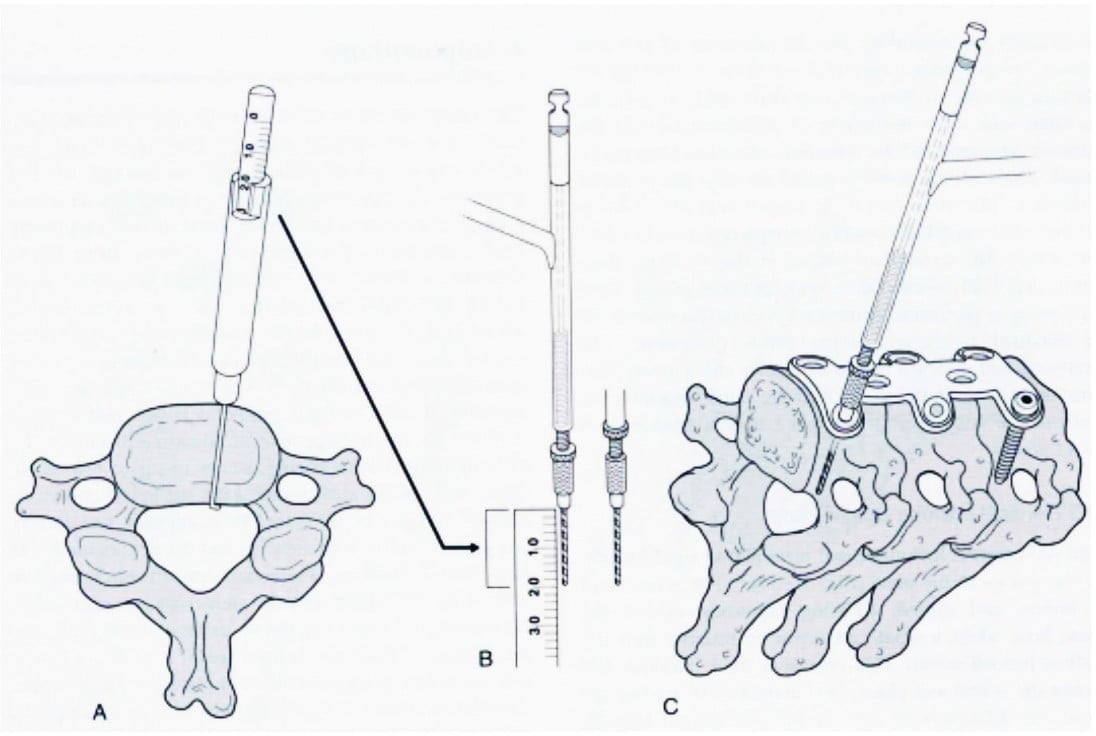
Figure 11.20. Front door screws