Table of contents [hide]
INJURY MECHANISM
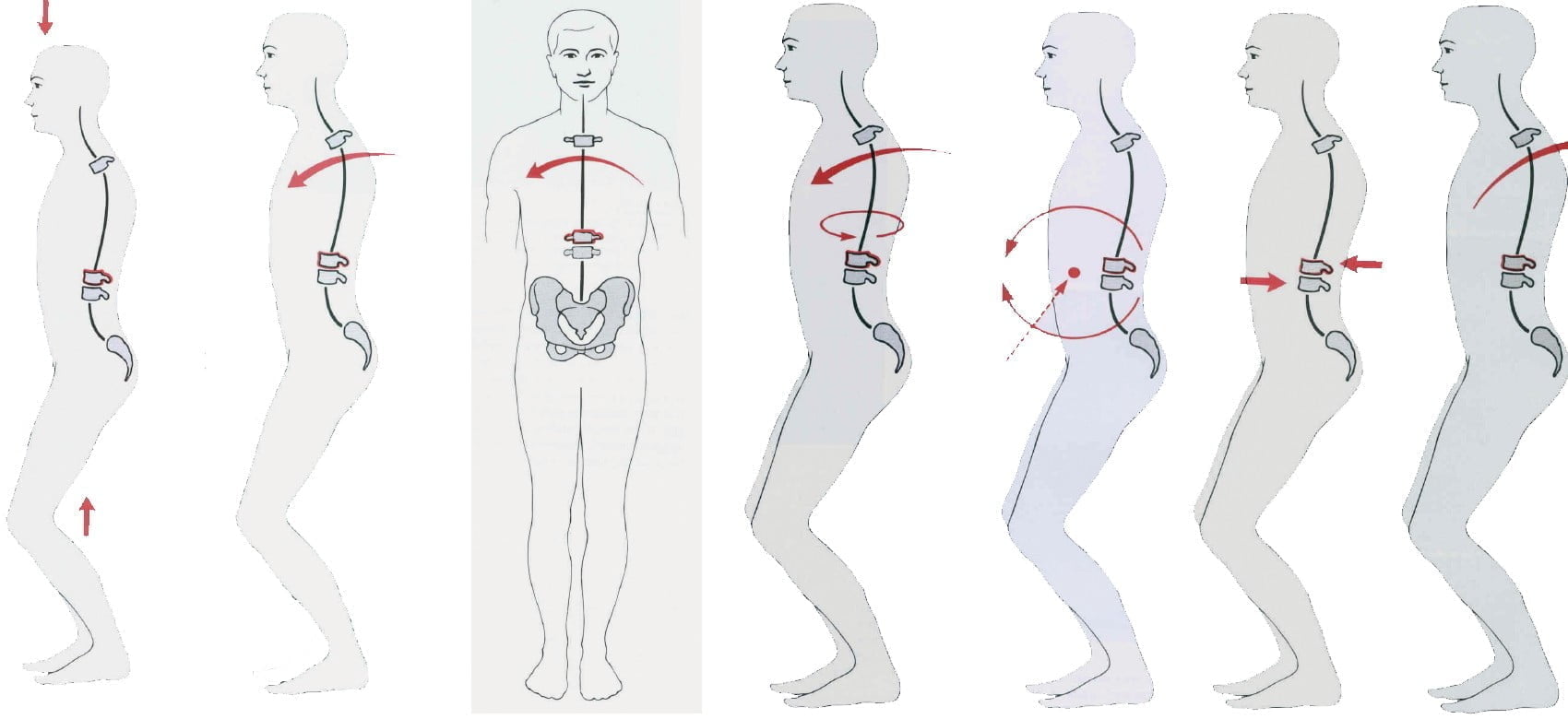
Figure 12.1. Mechanism of injury
1: Axis 2: Fold 3: Lateral compression 4: Rotational flexion 5: Tension flexion 6: Tear-tear 7: Stretch [1]
DENIS .'s 3-column and space concept
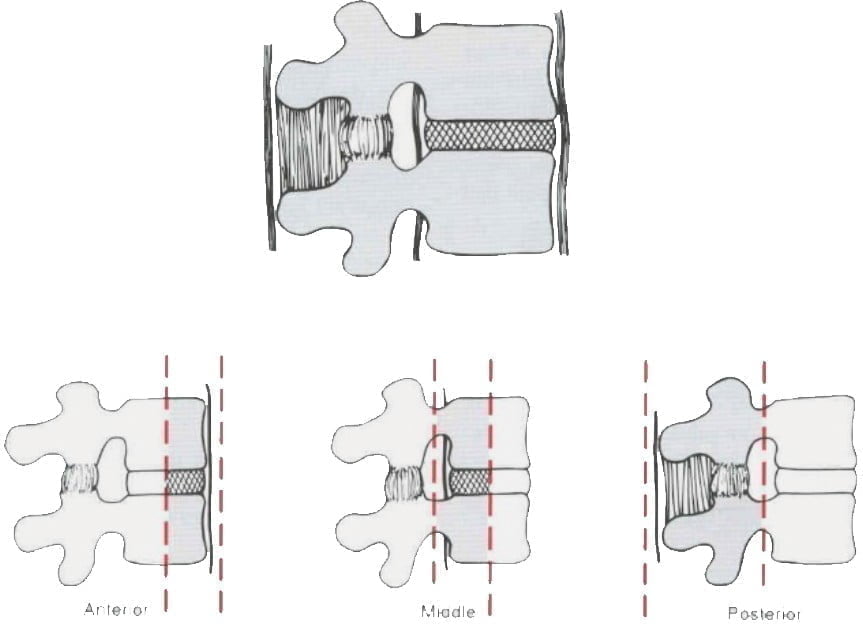
Figure 12.2. Three columns according to Denis [1]
– Stable: 1 . column settlement fracture
– Mechanical instability: from 2 to 3 columns but no paralysis: broken 2 anterior columns, tension folded fracture
- Unstable nerves: broken many pieces
– Mechanical and neurological instability: dislocation.
CLASSIFY
- Subsidence fracture (Figure 12.3)
- Multi-fragmentation (Burst Fracture) (Figure 12.4A)
- Flexion-Distraction (Figure 12.4B)
- Dislocation (Tear) (Figure 12.4C)

Figure 12.3. Subsidence fracture [1]
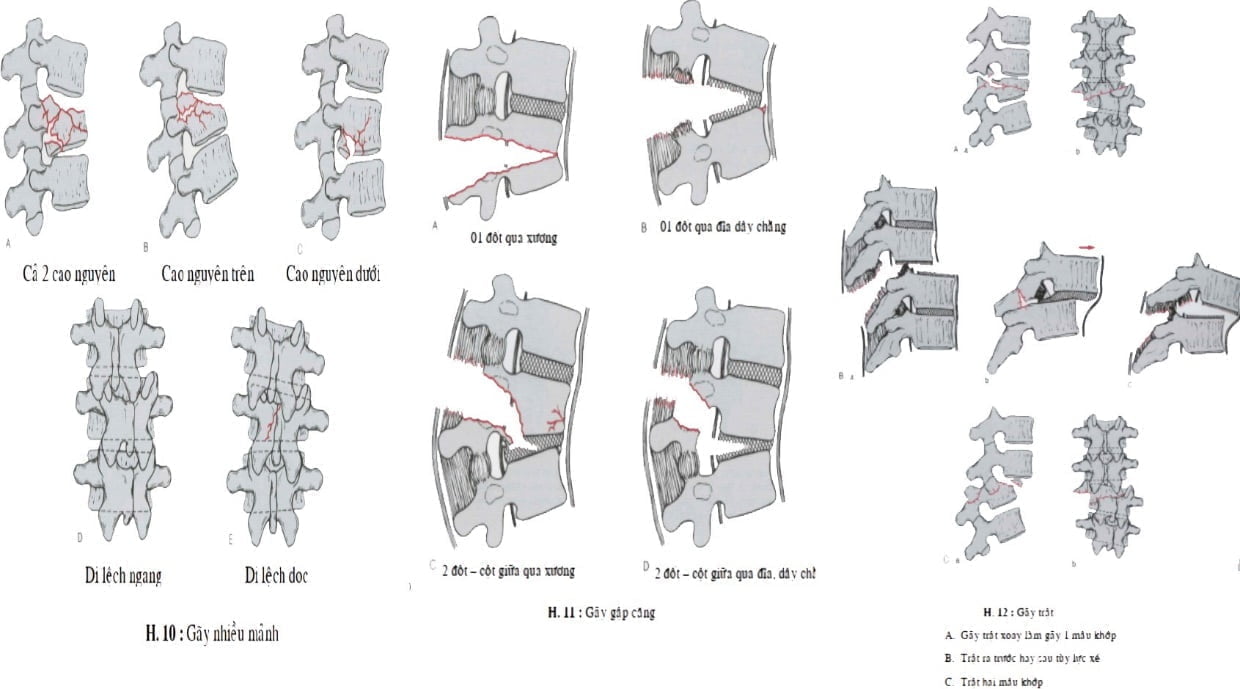
Figure 12.4. Multiple fractures, tension fractures, and dislocations [1]
TREATMENT
Strong fracture
Also known as subsidence fracture - conservative treatment.
- Stay in bed for 4 weeks
- Or 4 weeks thoracic-waist brace (Figure 12.5)
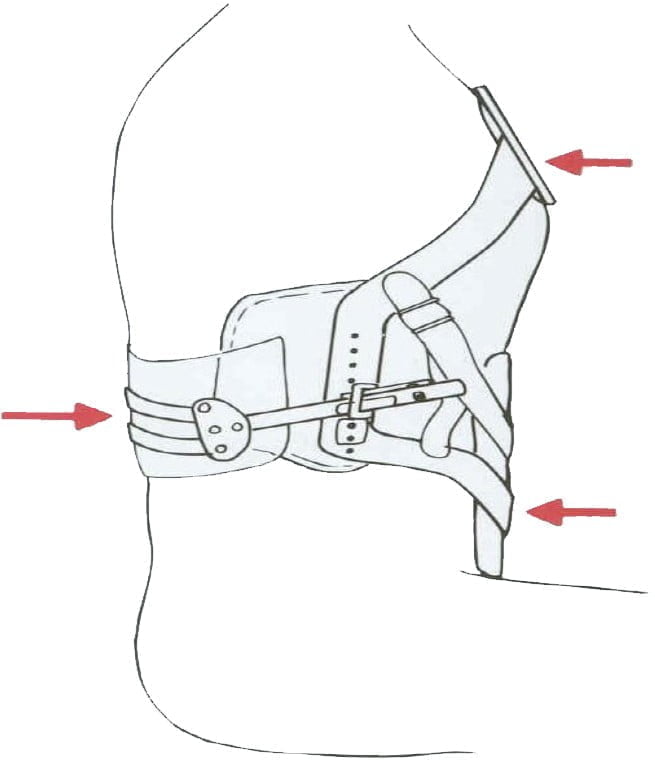
Figure 12.5. Chest brace – three-point belt
Mechanically unstable fracture (no paralysis)
2, 3 column fractures – tension flexed fracture.
- Conservative treatment such as 4.1
- Surgery: bone grafting (anterior or posterior) + bone fusion device (anterior or posterior) (Figure 12.6 and Figure 12.7).
Nerve instability (with paralysis): multiple fractures
Surgical treatment: decompression + anterior bone graft + bone fusion device (anterior or posterior) (Figures 12.6, 12.7).
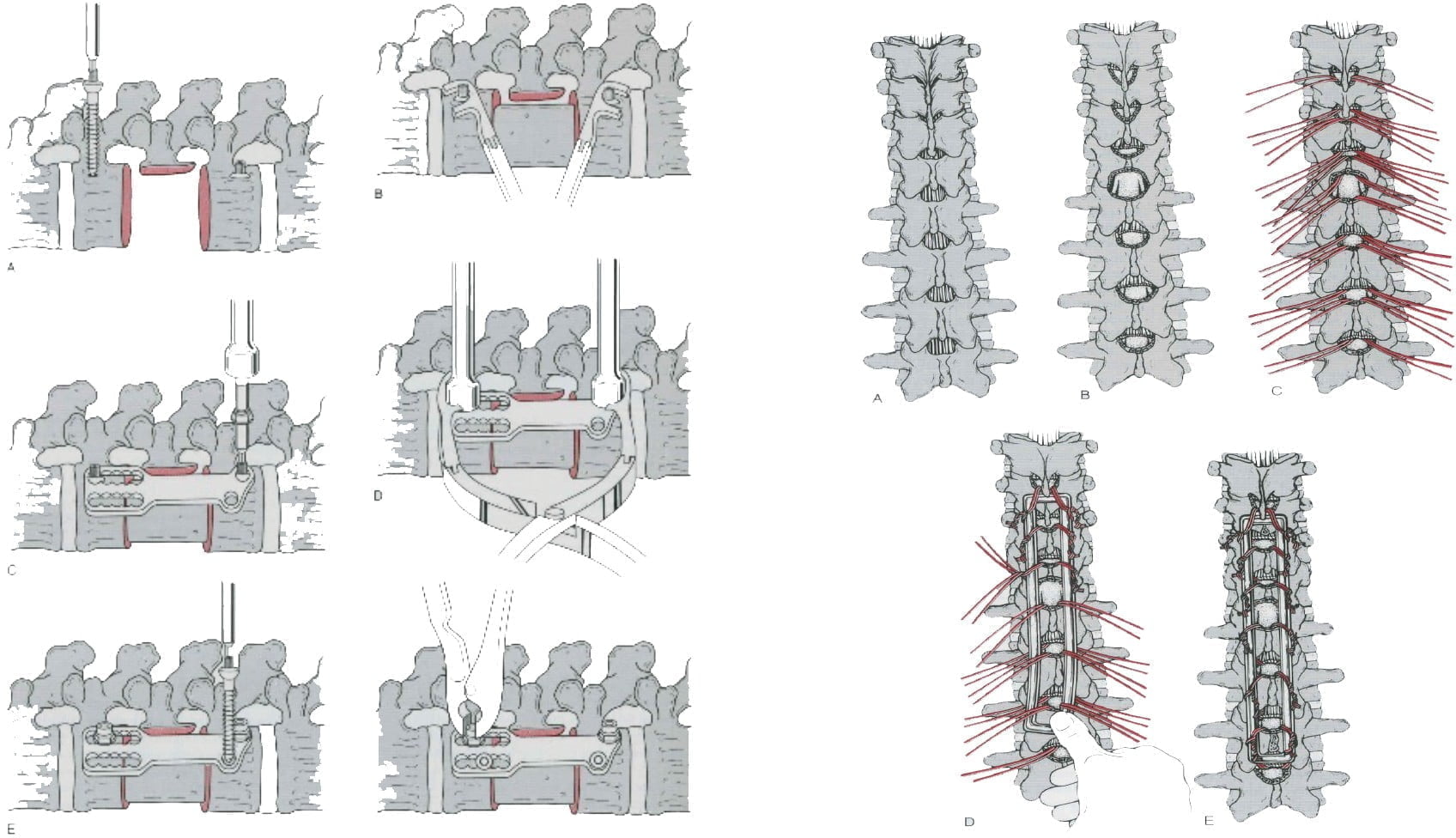
Figure 12.6. Bone graft surgery – combining bones in the front way Figure 12.7. Posterior bone fusion surgery
Mechanical and neurological unstable fracture: dislocation.
Surgical treatment: manipulation + bone grafting + posterior fusion (Figure 12.7).