Table of contents [hide]
GENERAL FEATURES
The cruciate ligament system consists of two anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments located along the longitudinal axis of the joint, crossing each other in both vertical and horizontal planes in the center of the joint. knee joint.
Anatomically, the two cruciate ligaments are located in the capsule and outside the kneecap.
![1 . Cruciate Ligament Injury Giải Phẫu Dây Chằng Chéo Trước [1]](https://bsvothanhtoan.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Giai-phau-day-chang-cheo-truoc-1-300x125.jpg)
![2 . Cruciate Ligament Injury Giải Phẫu Dây Chằng Chéo Sau [1]](https://bsvothanhtoan.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Giai-phau-day-chang-cheo-sau-1-300x91.jpg)
Ligament anterolateral cross is a thick and strong strand averaging 1.2 cm wide; average length of 3.5 cm extending from the medial surface of the lateral condyle of the femur to the anterior surface of the tibial plateau, behind the anterior horn of the meniscus inside, has the effect of keeping the tibial plateau from sliding forward.
The posterior medial cruciate ligament consists of bundles of fibers about 1.3 cm wide and 3.3 cm long extending from the lateral surface of the medial condyle of the femur to the posterior border of the tibial plateau, keeping the tibial plateau from sliding posteriorly.
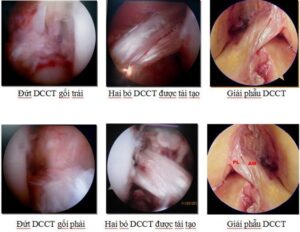
Injuries to rupture or detachment of the cruciate ligament may be associated meniscus tear, break lateral ligament. In fact, it is necessary to diagnose early and treat promptly and properly to avoid complications that affect the stability of the knee joint later.
CAUSE AND MECHANISM
- Direct trauma:
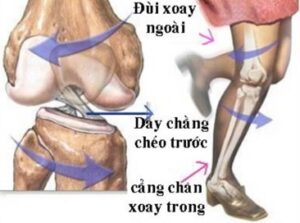
+ Injury force acting from the front, pushing back, when the knee is in the stretching position, it will break the anterior cruciate ligament, this mechanism is encountered in soccer.
![4 . cruciate ligament injury Cơ Chế đứt Dây Chằng Chéo Sau [4]](https://bsvothanhtoan.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Co-che-dut-day-chang-cheo-sau-4-300x194.jpg)
+ When the traumatic force is applied to the head on the two shin bones in the direction from front to back, in the folded knee position, the thigh is pushed forward, causing the posterior cruciate ligament to rupture, this mechanism is encountered in a car accident. machine pounding the shin against the roadside marker.
+ When the traumatic force is very strong directly hitting the knee joint, it can cause the entire knee joint to be injured such as knee dislocation, rupture of the tibial plateau and accompanied by rupture of the cruciate ligaments.
Indirect trauma has the same etiology and mechanism as meniscal tears and lateral ligament injuries.
Histopathology
- Location: for the anterior cruciate ligament, it can be detached at the attachment point to the tibial spine or break the body of the ligament. For the posterior medial cruciate ligament, it is common to break in the upper part of the attachment, but there are many cases of detachment of the cruciate ligament in the tibial plateau.
- The pattern of injury to the cruciate ligaments: The cruciate ligaments can be injured by only one ligament, but sometimes both ligaments are involved and can be accompanied by other injuries. Ligaments can be stretched only, partially ruptured, dislocated at the end point, and in many cases completely ruptured.
CLINICAL SYMPTOMS AND X-ray images
Clinical symptoms
– Subjective symptoms: after an injury to the knee joint, patients see:
+ Swollen knee joint
+ Decrease or almost complete loss of knee joint function
Pain in the joint, especially when flexing, extending, and rotating the leg.
Objective symptoms:
+ The knee joint has blood effusion, aspiration of the knee joint has hematoma. In cases of end-to-end detachment, the aspiration has a lot of blood and fat scum
+ Drawer sign: patient lying on his back, knee flexed 90o, groin folded 45o, immobilize the patient's foot by sitting, pressing on the front part of the foot. The examiner's hands go around the back of the lower leg, grasp the top of the tibia, and pull it forward or backward.
The drawer sign is positive when the tibial plateau is displaced anteriorly or posteriorly by more than 5 mm relative to the healthy side. Anterior displacement of the tibial plateau results in rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament and posterior displacement of the posterior cruciate ligament. If mobility is abnormal both anteriorly and posteriorly, both ligaments are ruptured
![5 . Cruciate Ligament Injury Khám Tìm Dấu Hiệu Ngăn Kéo Ra Trước, Ra Sau để Phát Hiện Tổn Thương Dây Chằng Chéo Trước Và Dây Chằng Chéo Sau [3]](https://bsvothanhtoan.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/Kham-tim-dau-hieu-ngan-keo-ra-truoc-ra-sau-de-phat-hien-ton-thuong-day-chang-cheo-truoc-va-day-chang-cheo-sau-3-249x300.png)
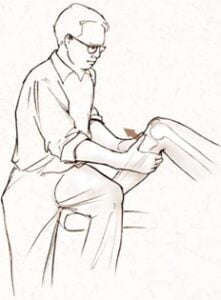
Lachmann's sign: the patient lies supine with the knee flexed 20-30 degreeso, the examiner uses the left hand to fix the lower head of the femur, the right hand to grasp the top of the tibia forward or backward. This sign is positive when the tibial plateau moves forward or backward more than the healthy side, the patellar tendon is prominent and there is a feeling that the knee is loose. In obese or recently traumatized patients, this finding is difficult.
X-ray
Take a shot X-ray knee joint straight, inclined; reclining position with a 45o flexed pillow; used as a drawer sign to assess tibial plateau displacement.
DEFINITION AND DIFFERENT DIAGNOSIS
- Definitive diagnosis: usually just based on clinical symptoms, especially drawer sign, is enough to confirm the diagnosis of cruciate ligament rupture. However, in many cases where the drawer sign and other examination are equivocal, endoscopic diagnosis is necessary.
- Differential diagnosis: with other knee injuries
+ Fracture of the lateral ligament: very clear positive sign of joint opening
Injury to meniscus: positive signs of joint entrapment and, if necessary, arthroscopy pillow for definitive diagnosis.
PROGRESS AND COMPLAINTS
Normal progression
For cases of partial rupture of the cruciate ligament or detachment of the attachment point of the ligament, if treated early and properly, it will Rehabilitation completely.
A complete tear of the cruciate ligament cannot heal on its own, but surgery to reconstruct the cruciate ligament or suture the cruciate ligament by endoscopic techniques, if done early, will bring results.
Symptoms
If the cruciate ligament is left untreated, it can lead to:
- Loose knee joints, long time causing inflammation and osteoarthritis pillow
- Limit the function of the knee joint.
TREATMENT
First aid
Once a diagnosis of a cruciate ligament injury is motionless Knee joint with a thigh-foot brace or a shallow thigh-ankle splint, then immediately transferred to the back for definitive diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Real treatment
- Conservative treatment:
- + Indicated for cases of incomplete rupture of the cruciate ligament, grade 1, grade 2 detachment of the cruciate ligament due to trauma (grade 1: the bone fragment of the cruciate ligament has only been dislocated, grade 2 : the cruciate ligament is partially pulled up).
- + Các trường hợp này điều trị càng sớm càng tốt, điều trị bằng chọc hút máu trong khớp gối nếu có, cast đùi – cổ chân gối gấp 10O trong 6 – 8 tuần.
- Surgical treatment: reconstructive surgery of the cruciate ligament by many methods.
- + Method of reconstructing the cruciate ligament by the long fibula tendon, by Hey-Grove's fascia strain; using H. Bruckner's quadriceps tendon; using Kennet-John's patellar tendon, semi-tendon tendon, twin muscle.
- + If both cruciate ligaments are torn, two cruciate ligaments can be reconstructed at the same time.
- + In the case of extraction of the tibial attachment point of the anterior cruciate ligament, it is possible to sew and fix the attachment of the ligament through laparoscopic surgery.