Table of contents
OUTLINE
Definition of fracture
Fracture is the sudden destruction of the internal structures of the bone due to mechanical causes. Injury to bone structure (periosteum, bone and spinal canal) and tissues surrounding bone such as tendons, blood vessels, nerves.
Classification of fractures
- Closed fracture: fracture without skin wound or wound but not open to fracture (hematoma).
- Open fracture: A fracture has a skin wound and this wound penetrates the fracture site.
Clinical signs
- Sure signs:
- limb deformation
- Abnormal movements
- Crackling sound.
After an injury, if you see one or more of the above signs, you can definitely say that there is a fracture.
- Uncertain signs:
- Painful
- Swollen, bruised
- Loss of ability.
All cases of fractures have the above symptoms. But other injuries (such as dislocation, sprains,…) also have these signs, so it is difficult to confirm whether it is a fracture or not.
Pictographic signs
- Take a shot X-ray Conventional convention for all fractures: at least two planes (facial and lateral), full capture of two joints of a long stem, other positions if necessary
- Computed tomography (CT-scan) for complex fractures
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is rarely used. Especially when it is necessary to see details of injuries: facet joints, meniscus, soft tissues such as muscles and ligaments.
Symptoms
- Early complications:
- Shocked (shock) trauma
- Blood vessel occlusion due to fat
- Cavity compression
- Injury to the main blood vessel
- Major nerve damage
- Infected open fracture.
- Late complications:
- Nutritional disorder
- Inflammation of the bone
- Complications bone healing:
- Misalignment
- Prosthetic joints and slow healing.
PURPOSE AND PRINCIPLES OF IMPROVED BACKGROUND
Purpose
- Pain relief, prevention of shock and trauma
- Reduce the risk of further damage: blood vessels, nerves, skin, muscles, turning closed fractures into open fractures, etc.
Rule
- Evaluation: motor sensory circuit of the extremities before and after immobilization. Expose, evaluate (possibly take pictures) of the affected area before fixing
- The splint should be long enough for a firm immobilization. Immobilize one joint above and one below the fracture. Immobilization above and below the injured joint
- Tie the brace securing the right brace over the break, below the break, above the joint, and below the joint
- Do not try to insert the exposed bone back into the skin
- Immobilize the limb in a functional or comfortable position. For upper extremities flexed 900, for lower extremities flex the knee in a 10-20 . positiono
- If the limb is deformed, flexes a lot, cannot catch the pulse below the injury site, the limb is purple, cold, it can be pulled back to the anatomical position before fixation. If you have to straighten the limb back to the anatomical position, it is necessary to use pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and both straighten and stretch. When pulling, use gentle force, do not try to straighten when entangled or stuck.
- For open fractures, immobilize after dressing. If there is damage to the blood vessel, it is necessary to apply pressure to stop bleeding before immobilization
- Do not place the splint directly close to the patient's skin, the convex bone positions must be lined with cotton, the brace must be fixed tightly
- Elevate the limb after immobilization (if there are no contraindications).
INSTALLATION OF SOME FREQUENT BACKGROUND
Immovable tools
- Cramer (Kramer) brace (Figure 14.1) made of steel, can be bent to the required positions
- Rubber brace: made of double-layer rubber with valve for inflating
- Wooden splint: use a smooth planed wooden stick, different sizes depending on the upper and lower limbs
- Actual custom splint: bamboo, wood, materials available
- Cotton bandage: used to line the support point of the brace, if not, use soft paper or cloth
- Fabric, lanyard to fix the brace.
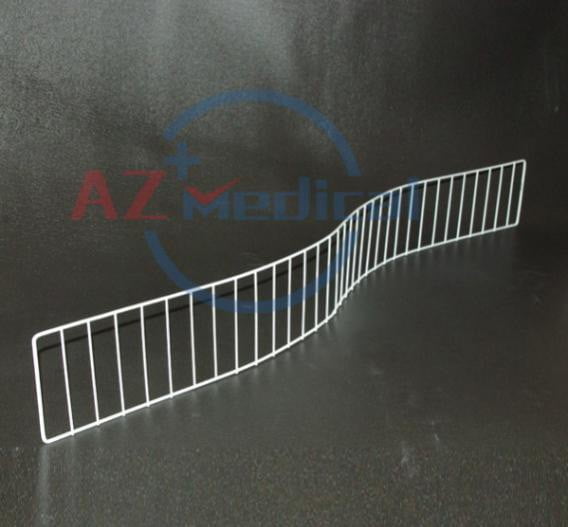

Figure 14.1. Cramer Splint (Kramer) [1]
Immobilize the cervical spine
Absolutely do not move the patient, do not allow the patient to sit up. Limiting secondary displacement when transporting patients with suspected fractures cervical spine.
- Quickly and gently bring the victim to safety
- Place the victim on a hardboard
- If there is a neck brace (Collar brace) (Figure 14.2), immobilize the patient's cervical spine immediately
- Immobilize the victim to a hard board. Do not tilt the victim's head to the side or bend the neck. When necessary, the patient must keep the spine - neck - head straight. Use the coil to immobilize the victim to the hardboard in the following positions: forehead, jaw, chest, hips, thighs, knees, shins, feet (Figure 14.3).
- Wedge soft pillows on both sides of the victim's neck.
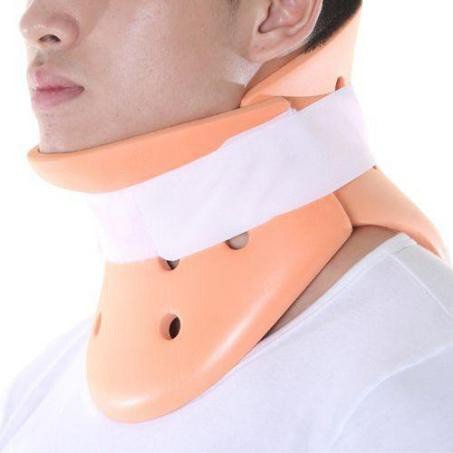
Figure 14.2. Splints Collar [1]
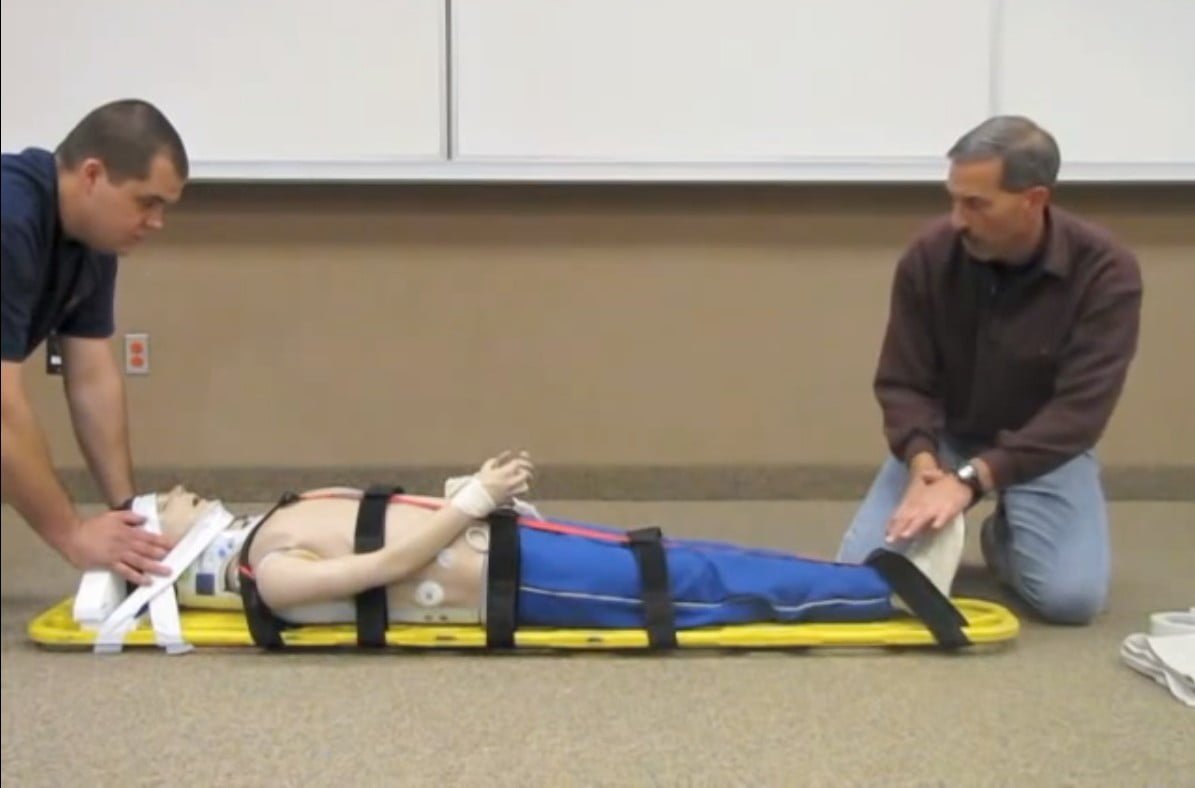
Figure 14.3. Immobilize the victim on a hardboard [1]
Immobilize the collarbone and shoulder blades: Use a 10-12cm wide elastic band to fix the two collarbones rear cross back (Figure 14.4; Figure 14.5) and immobilize the shoulder blades with a cloth brace to fix the shoulder and arm areas as shown in Figure 14.6.
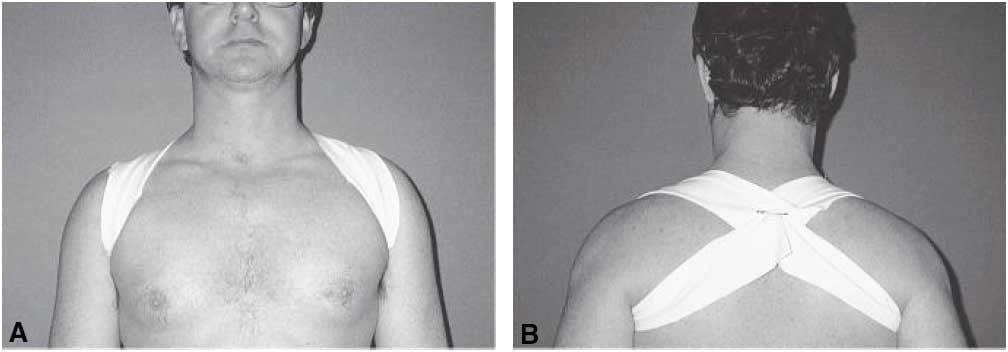
Figure 14.4. Clavicle immobilization with webbing [1]
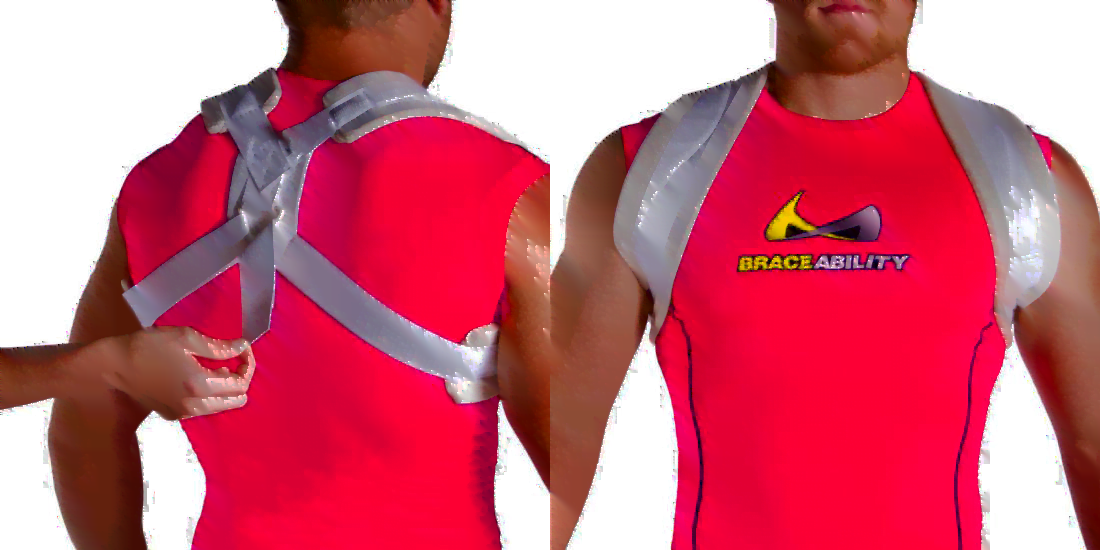

Figure 14.5. Clavicle fixation belt [1]
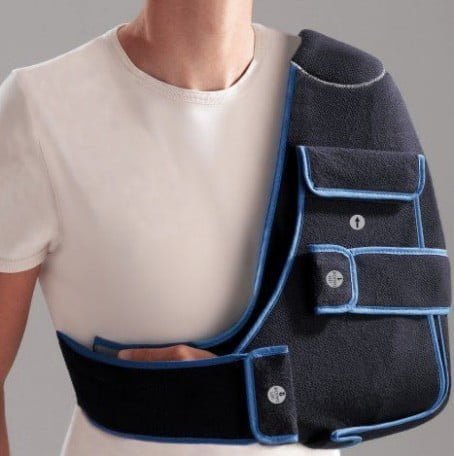

Figure 14.6. Shoulderless tops [1]
Rib fixation: if only single rib fracture, no mobile rib plate, no chest trauma. Just relieve the patient's pain, go to the hospital for monitoring, and leave the hospital after consulting with a specialist in surgery.
Arm bone fixation
- Using a forearm fabric brace, where this is not available, two splints can be placed (Figure 14.7):
- An internal splint, the upper end up to the axillary fossa, the lower end over the elbow
- An external splint, the upper end over the shoulder, and the lower end over the elbow.
- Then the bandage fixed, forcing the arm to the body
- Use a triangle bandage to hang the victim's arm and tie it to the chest.

Figure 14.7. Motionless broken arm bone [1]
Stabilization of forearm bones
- If elbow joint contract, bring the arm close to the torso, forearm perpendicular to the arm, then immobilize (Figure 14.8)
- Đặt hai thanh nẹp mặt trước và mặt sau cánh tay. Cả hai nẹp đều dài quá khuỷu tay tới đầu các ngón tay
- Wedge cotton or fabric to the pressure point. Tie the brace fixed
- Hang your hands around your neck in an upward position and force them to your body.
- If elbow joint is not flexed, keep arm straight, then immobilize (Figure 14.8)
- Place splint from armpit to hand
- Use tape to fix the brace.
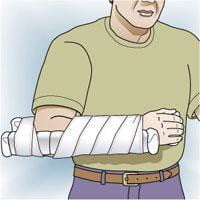
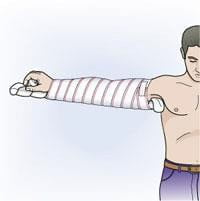
Figure 14.8. Immobilization of broken forearm wooden splint [1]
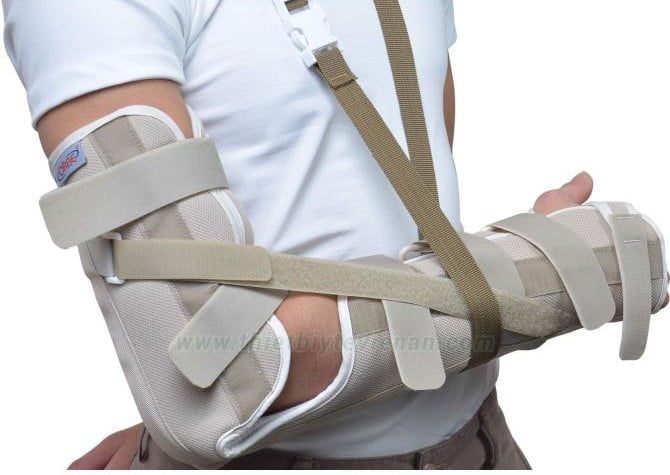
Figure 14.9. Immobilize the forearm fracture with a cloth brace [1]
Fixed wrist, hand, finger
Immobilize the wrist fracture, the hand proceeds as if the forearm fracture is immobilized but the hand is facing down (Figure 14.10).
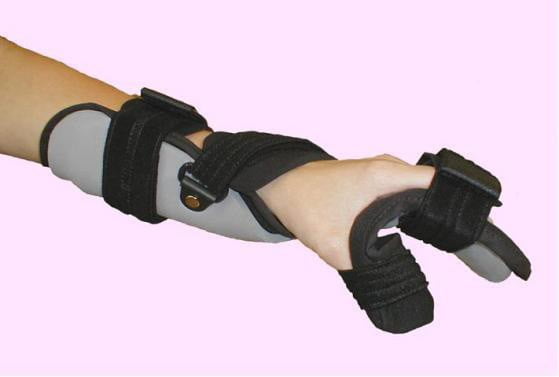
Figure 14.10. Wrist and hand immobilization brace [1]
- Immobilize the finger bones with a small wooden splint, an Iselin brace, or tie the fingers together (Figure 14.11).
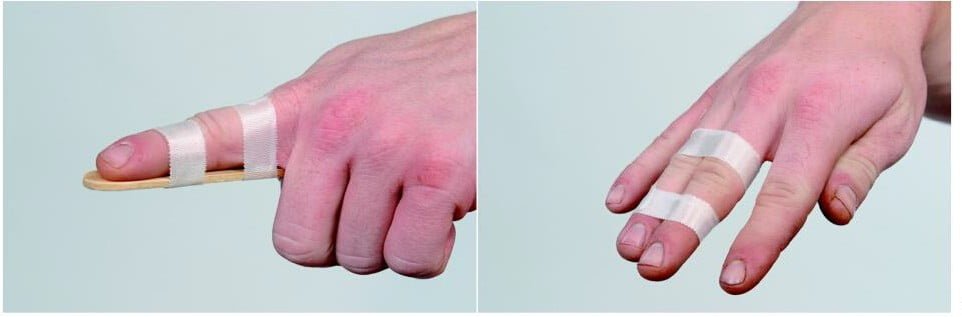
Figure 14.11. Finger immobilization brace [1]
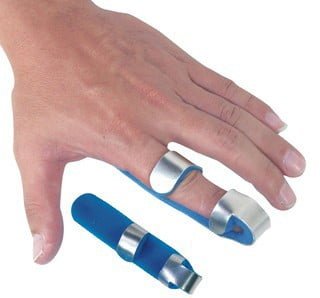
Figure 14.12. Iselin Finger Splints [1]
Stabilize shin bones
- Help the victim lie on his back
- Use a cloth brace or place two wooden braces:
- An internal splint, the upper end close to the groin, the lower end past the medial ankle
- A brace from mid-thigh to outer ankle
- Insert cotton or soft cloth into pressure areas
- Firmly fix the two splints, tie the legs together at the following positions: above the knee, close to the knee and close to the ankle.
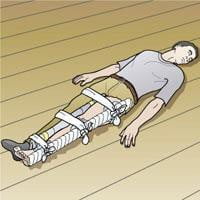
Figure 14.13. Immobilization of broken shin splints [1]
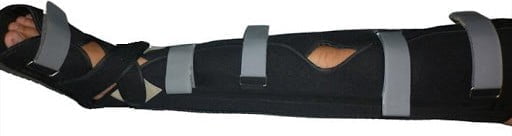
Figure 14.14. Immobilization with a femoral splint [1]
Stabilize the femur
- Help the victim lie on his back
- Use an anti-rotation thigh brace or place three wooden braces:
- An inner brace from the ankle to the groin
- An external splint from the ankle to the axillary fossa
- A rear brace from heel to butt
- Wedge cotton or soft cloth to the pressure points
- Firmly fix the three splints to the limb and trunk in positions below the armpit, iliac crest, above and below the fracture, below the knee, and the ankle. Tie the immobilized broken limb to the healthy limb.
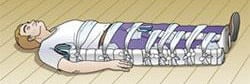
Figure 14.15. Immobilize femur fractures with wooden splints [1]
- Nếu không bắt được mạch dưới chỗ tổn thương, phải dùng nẹp kéo liên tục như nẹp Thomas, Sager, Hare
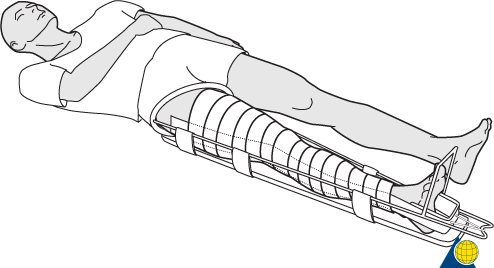
Figure 14.16. Thomas Splint [1]
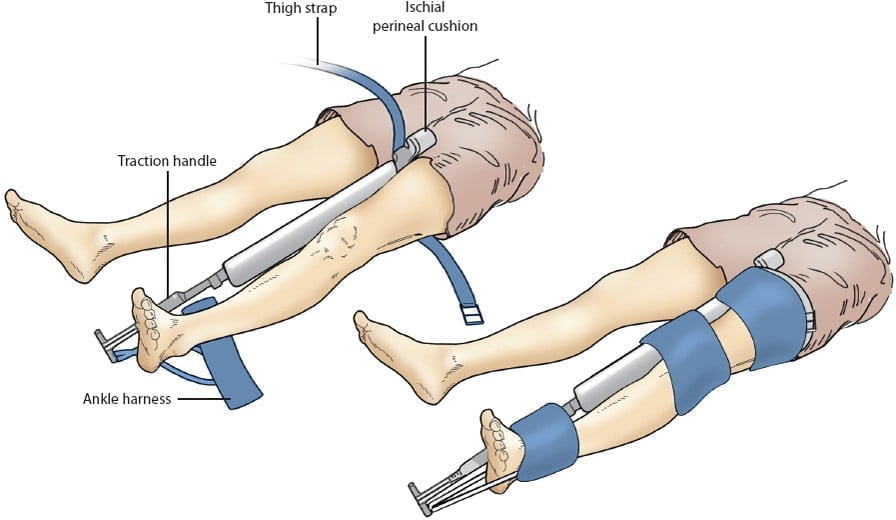
Figure 14.17. Sager Splints [1]
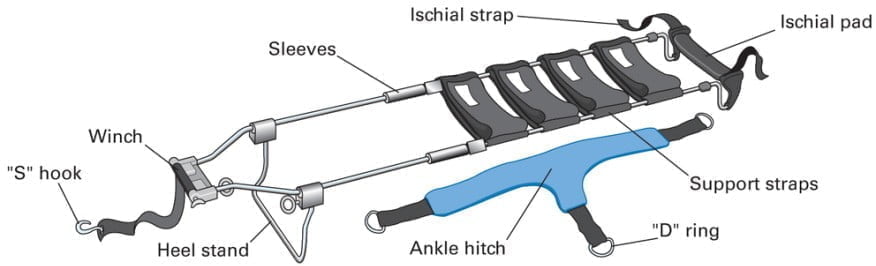
Figure 14.18. Hare Splint [1]
Stabilize ankles, feet, toes
- When immobilizing the ankle, the foot needs to keep the foot in the correct functional position, place the L-brace under the foot and shin, and then tie the fixed rope.
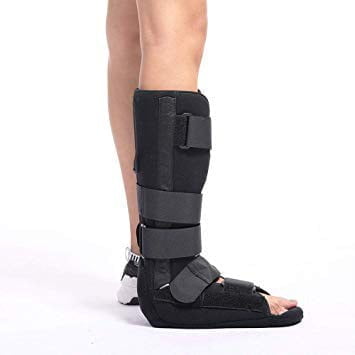
Figure 14.19. Ankle splints, feet [1]
- Immobilize the toe by tying the toes together
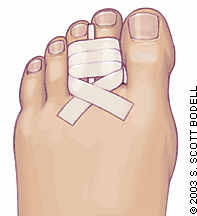
Figure 14.20. Toe immobilization [1]